|

|
Liquid Crystals and their Application
Russian Journal Zhidkie kristally i ikh prakticheskoe ispol'zovanie Жидкие кристаллы и их практическое использование |

|
|

|

|
|
|
Menu

|
|
|
|
|
Zhidk. krist. ikh prakt. ispol'z. = Liq. Cryst. and their Appl., 2016, 16 (1), 105—113.
DOI: 10.18083/LCAppl.2016.1.105 |

|
|
Non-Newtonian Flow of Structured Systems.
XVI. Viscosity Curves of Polymer Melts
|
E. A. Kirsanov, Yu. N. Timoshin
|
Author affiliations
Moscow State Region Socio-Humanitarian Institute,
30 Zelenaya St., Kolomna, Moscow Region, 140411, Russia
E-mail: Kirsanov47@mail.ru
|
AbstractGeneralized flow model is used to describe viscosity curves and flow curves of polymer melts, namely, low density polyethylene, polystyrene with broad molecular weight distribution, polycarbonate, and polypropylene. This model is a structural rheological model, which is the alternative with respect to the known models of theoretical rheology. Structural model predicts the temperature dependence of the three coefficients of the generalized flow equation: η c∼exp(B/RT), χ∼exp(-D/RT), τ c=cost. Different flow regimes (namely, Newtonian flow, pseudoplastic flow and spurt of flow) are considered. The presence of large transition intervals between flow regimes makes it difficult for the interpretation of the viscosity curve. Rheological curves must be regarded in three different types of coordinates for a better analysis of the flow: 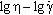 , 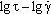 , 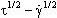 . Keywords: polymer melts, structural rheological model, flow regimes, the temperature dependence of the coefficients
|
|
|
|
|
|




