|

|
Liquid Crystals and their Application
Russian Journal Zhidkie kristally i ikh prakticheskoe ispol'zovanie Жидкие кристаллы и их практическое использование |

|
|

|

|
|
|
Menu

|
|
|
|
|
Zhidk. krist. ikh prakt. ispol'z. = Liq. Cryst. and their Appl., 2017, 17 (4), 73—82.
DOI: 10.18083/LCAppl.2017.4.73 |

|
|
Non-Newtonian Flow of Structured Systems.
XXIV. Shear Thickening
|
E. A. Kirsanov, Yu. N. Timoshin
|
Author affiliations
State University of Humanities and Social Studies,
30 Zelyonaya St., Kolomna, 140411, Moscow Region, Russia
E-mail: Kirsanov47@mail.ru
|
AbstractWe have considered the features of shear thickening, that is, the phenomenon of increase in the suspension viscosity with increasing the shear rate after exceeding the critical shear rate. We have shown that viscosity curves (flow curves) are well approximated using the generalized flow equation 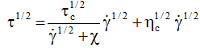 on the interval before the onset of shear thickening and on the interval after the completion of the shear thickening. We used published experimental results for structured systems: an aqueous suspension of corn starch, a suspension of carbon black particles in tetradecane, a suspension of particles of polymethylmethacrylate in polyethylene glycol, colloidal dispersion of silicon nanoparticles in polyethylene glycol. After the phenomenon of shear thickening is complete, a "flow spurt" is sometimes observed. The value of the critical shear rate 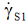 of the transition from shear thinning to shear thickening decreases with increasing concentration of the dispersed phase. Within the framework of the structural rheological model, the phenomenon of shear thickening is interpreted as a transition from one flow regime to another regime, associated with an increase of the engagement force between particles. Keywords: structural rheological model, shear thickening, suspensions
|
|
|
|
|
|





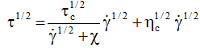 on the interval before the onset of shear thickening and on the interval after the completion of the shear thickening.
on the interval before the onset of shear thickening and on the interval after the completion of the shear thickening.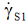 of the transition from shear thinning to shear thickening decreases with increasing concentration of the dispersed phase. Within the framework of the structural rheological model, the phenomenon of shear thickening is interpreted as a transition from one flow regime to another regime, associated with an increase of the engagement force between particles.
of the transition from shear thinning to shear thickening decreases with increasing concentration of the dispersed phase. Within the framework of the structural rheological model, the phenomenon of shear thickening is interpreted as a transition from one flow regime to another regime, associated with an increase of the engagement force between particles.